Blockchain technology is gaining popularity around the world. Companies and individuals around the world are leveraging blockchain for a variety of purposes.
Blockchain is spreading its wings in all dimensions, including cryptocurrencies, IT, and healthcare.
However, this concept is still new to most people in the world. While many people are still ambivalent about the security and reliability of blockchain, some want to explore the concept further.
If you are interested in learning this technology, it is important to understand blockchain nodes. If you are a business or blockchain enthusiast looking to develop secure and affordable blockchain-based solutions, knowledge about blockchain nodes will come in handy.
Now, let us understand blockchain nodes and their types in detail.
What is blockchain?
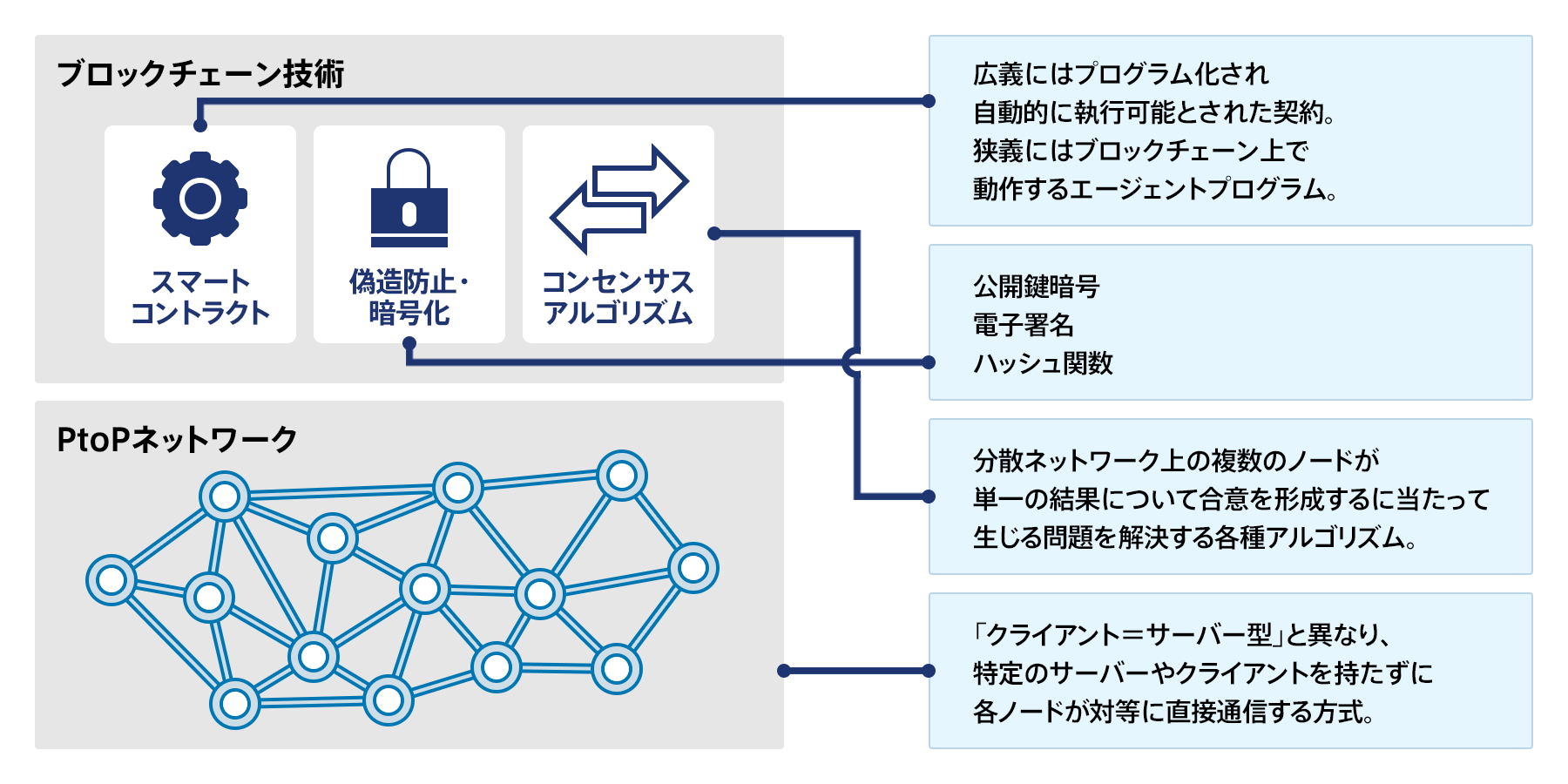
Blockchain is an immutable shared ledger that stores transactions and tracks assets within a network. This is a database where data is arranged in blocks rather than rows and columns as found in traditional databases.
The term “blockchain” is derived from two words: “block” and “chain.” Each verified transaction or record in the blockchain network is added to a block with a defined space. Once this space is filled, new verified records are added to the next block and cryptographically connected or “chained” to the previous block.
Blockchain technology was invented in 2008 by the unknown Satoshi Nakamoto.
Its main elements are:
- Decentralization : Blockchain is a decentralized system, meaning no one person owns it and anyone can access it with permission. It is also known as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) because it is a distributed ledger that contains related records and allows users to store, share, and perform peer-to-peer transactions.
- Immutability : Each record in the blockchain is timestamped to avoid tampering and double records. If a record has an error, you must add a new record with the corrections so that both records are visible.
- Transparency : Most blockchains, except for private blockchains, are open source and have no central authority. Therefore, anyone can access that code and suggest changes, increasing mutual trust and transparency among the members of the network.
Blockchain technology is used in a variety of industries, from banking and finance to IT, supply chain, and healthcare. Its usage is rapidly increasing, with companies using the technology in video games, smart contracts, document verification, payments, and more. It’s not only safe, cost-effective, and easy to use, it’s also faster and more accurate.

What is a blockchain node?
A blockchain node is an electronic device with an IP address and is connected to the blockchain network via the internet. Nodes are communication endpoints that allow users to interact with the blockchain.
Nodes allow a blockchain system to run. It’s like a playground where everything happens. This playground consists of multiple blockchain platforms: private, public, or hybrid.
Blockchain nodes can perform different functions based on the requirements of the blockchain. Some basic tasks you can perform include:
- Facilitating communication
- Approve or reject a transaction
- Transaction processing
- Managing transactions
- Block storage in conjunction with cryptography

Why do we need blockchain nodes?
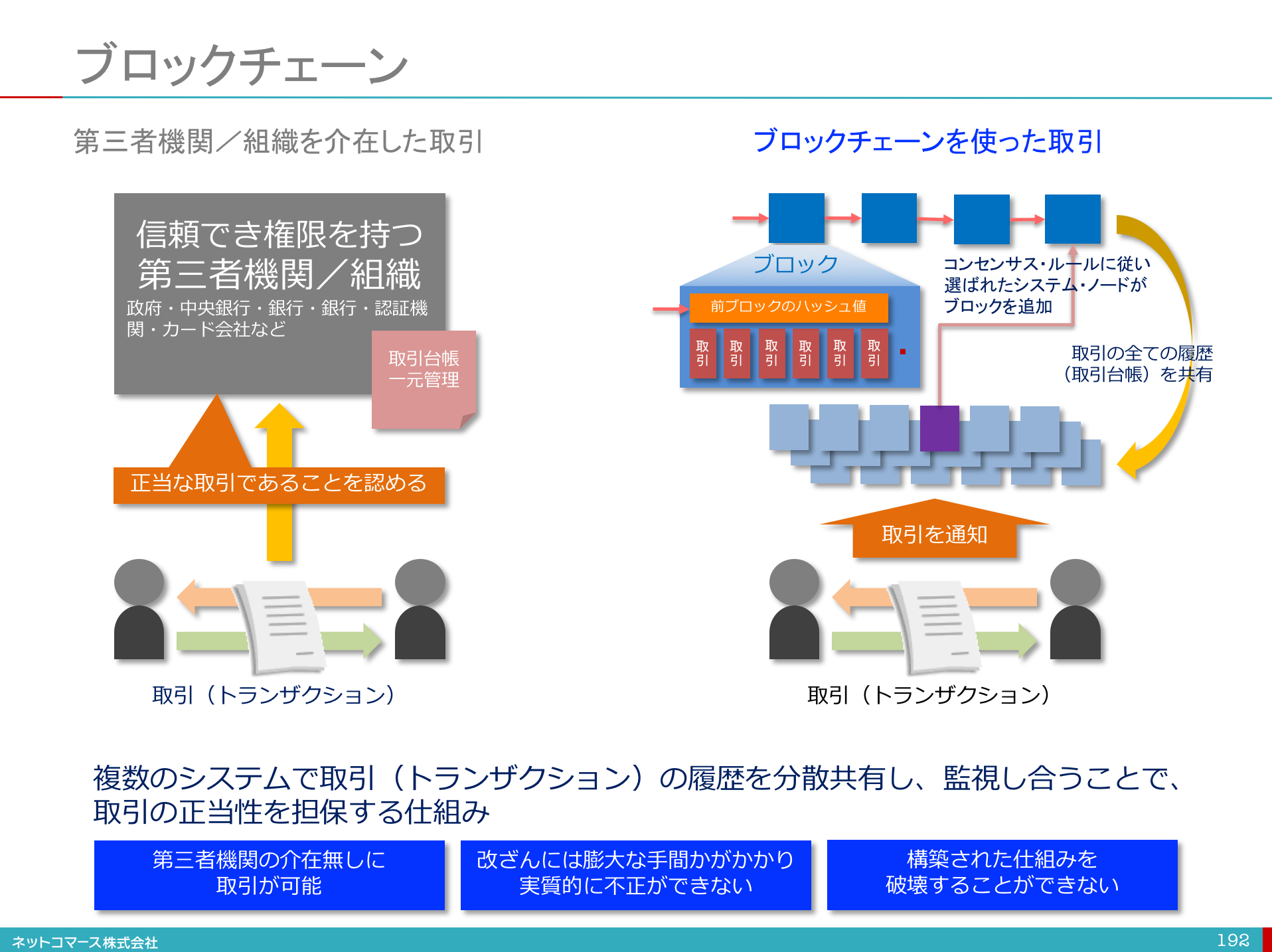
Blockchain technology ensures data integrity and increases network reliability. Therefore, the same ledger is distributed globally across multiple systems.
Every block containing data in the blockchain is connected to subsequent blocks through cryptography, so if you want to change a record or block, you must change all subsequent blocks. This is done to maintain accuracy and consistency, as each block contains a hash of the previous block.
So imagine if your blockchain network is limited to one location. It becomes easier for hackers to change block values and exploit the network. This is why blockchain is distributed around the world without a central hub to manage it. Therefore, the concept of decentralization was implemented.
Additionally, all connected systems or nodes spread around the world share the same data to maintain data integrity and accuracy in the network. Even if one system’s ledger is modified, other systems containing this ledger remain untainted and serve as evidence of data integrity. Globally distributing the blockchain across multiple nodes increases reliability while also making the network more resilient to attacks and natural disasters.
You need blockchain nodes to:
- Enabling access: Blockchain nodes allow users to easily access the blockchain ledger. This allows you to seamlessly interact with the network, allowing you to view transactions occurring within the network, view transaction details, and review records.
- Maintaining the blockchain: Nodes maintain the blockchain network and help it grow. Each data block in the blockchain is added to the storage of a node. The nodes are then used to add new blocks to the network and synchronize the data while maintaining a copy of the ledger. Final approval to add a block to the blockchain requires consensus by a majority of members.
- Transaction processing : When a transaction occurs within the blockchain, it is sent to that node. Based on their role, some nodes participate in the network’s consensus algorithm, while other nodes are responsible for record-keeping.
Upon receiving a transaction request, a node can accept or reject the transaction. This data can be stored and sent back to peers in the network. Nodes can also share data with other nodes in the network to facilitate synchronization.

How do blockchain nodes work?
So far, we have seen that blockchain technology maintains data integrity. But what’s actually going on behind the curtain is what we’ll learn next.
To maintain data integrity, everyone in the network must know that each transaction is valid and there is no double-recording that facilitates fraud.
Since there is no central authority governing the network, members must reach consensus to ensure that a transaction is valid. Network nodes enable this between users and ensure the security of the blockchain.
Consensus can include a set of rules for operating a blockchain and verifying the validity of data. Because blockchains can be large, with a huge number of systems and users, consensus algorithms are needed to verify the information in the blocks. Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are common consensus algorithms that rely on nodes (full nodes) to enforce network rules and validate transactions.
Example: Bitcoin uses PoW algorithm. Anyone can download the Bitcoin blockchain and verify blocks. This enables network decentralization and improves security. This blockchain allows anyone with a stable internet connection and suitable hardware to run a Bitcoin node.
Types of blockchain nodes
There are different types of nodes that provide different functionality. Users who interact with a blockchain network can also be called nodes. However, not all devices in a blockchain network are nodes and perform the same functions.
Nodes in a blockchain network are classified according to their role and blockchain requirements. For example, one node can be used to maintain transaction records even if no other nodes perform this task.
A blockchain can contain different nodes such as users, clients, and service providers.
Let’s take a look at the different types of blockchain nodes.
#1.Full node
A full node is responsible for maintaining the entire transaction record within the blockchain network. These are considered the servers of the blockchain where data is stored and maintained.
There are several blockchain governance models that full nodes can apply. If we make any improvements to the blockchain, we need to ensure that the majority of full nodes are ready for it. Therefore, we can conclude that full nodes are given voting rights to make changes to the blockchain.
However, certain scenarios can also occur if changes are not implemented even after a majority of full nodes agree to them. It can happen when you have to make a big decision.
For example, about 52% of full nodes agree to the change, while 48% disagree (which is close enough). In such cases, a hard cryptocurrency fork may occur where the blockchain is split in half, an action that is not backward compatible. When this happens, the newly created blockchain will function based on the changes proposed by the majority of full nodes, while the old blockchain will continue to function as before.
There are two types of full nodes.
pruned complete node
Pruned nodes are given a certain amount of memory to store data. This means that you can add any number of blocks, but a full node can only store a limited number of blocks.
To maintain the ledger, a pruned node can continue downloading blocks until it reaches a specified limit. Once the limit is reached, nodes will start deleting the oldest blocks to maintain the size of the blockchain and make space for new blocks. Nevertheless, in accordance with an important principle of blockchain technology, old blocks are not completely deleted, as their sequences and metadata are still recorded on the blockchain.
archive full node
This type of full node is commonly found in blockchain networks. Archive full nodes maintain the complete blockchain and differ from pruned full nodes in terms of memory capacity. These nodes come in different types.
- Minor nodes: Certain nodes are required to perform advanced calculations and solve complex mathematical functions to validate records. This requires a large amount of computing power and consumes a large amount of energy in the process. Miner nodes are ideal for mining processes that involve consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work.
- Authority Node: Anyone can become a member or node of a public blockchain by synchronizing blockchain data in the system. However, in some cases, you need to manage your blockchain and protect your data. This is where authority nodes come into play. These are used to authorize other nodes who wish to join the blockchain network. You can also define permissions for other nodes if you want to access specific data channels.
- Master node: A full node that does not have permission to add new blocks to the network. These are used to maintain ledgers and verify transactions.
- Staking nodes: These nodes are responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the consensus algorithm within the blockchain network. Proof of Stake (PoS), a well-known algorithm, uses staking nodes to stake or invest funds and validate transactions. If your transaction is successfully verified, you will receive some rewards in return.
Staking nodes are selected based on defined rules, such as time spent on the blockchain network. These complete nodes do not require large amounts of computing power.
#2.Light node
Light nodes are used to store data and provide only the information needed to facilitate daily tasks or enable faster transactions. These nodes are also known as Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) nodes. These nodes do not validate blocks. Instead, just store the header of the block.
#3.Super node
Supernodes are used to perform certain special tasks and are implemented in some blockchains. It can be used to set or maintain blockchain rules and implement protocol changes.
#4.Writing node
Writing nodes build users and individuals and push all transactions to the main blockchain. This reduces the load on the network, thereby reducing transaction costs while facilitating instantaneous transactions.
These types of nodes were created to solve the problem of congestion in blockchain networks that delays transactions.
FAQ
Answer: To set up a full node, you need to perform the following steps:
1. Choose a blockchain network such as Bitcoin or Ethereum.
2. Obtain the necessary software and hardware to run your chosen blockchain. You can find information online. The required hardware may include a small system such as a Raspberry Pi.
3. Configure all hardware and software.
Answer: Here are the steps to run a full node:
1. Host your nodes on a cloud-based service such as Google Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), or DigitalOcean.
2. Run the node on a device with sufficient RAM and storage space.
3. You can also build a “node-in-a-box” solution or use a dedicated solution.
4. Continue to monitor and maintain your nodes to ensure they are operating properly and secure.
Answer: Yes, you can make money by hosting a node on a blockchain network. However, it depends on the type of node you choose to host.
Hosting a staking node can be profitable. It can be your source of passive income. The more you invest, the more you earn.
If you choose to host a masternode, you can earn money for the services you provide. However, an initial investment in a masternode is required.
Answer: The number of nodes you can run on a machine depends on the capabilities of its hardware. Only one wallet instance can be running in a machine at a time. However, you can increase it by using virtual machines. Additionally, if you use a virtual private server (VPS), avoid exceeding 80-85% of your available server resource limits. Otherwise, you may be restricted or limited by your service provider.
conclusion
Knowledge about blockchain nodes and their types can help you create cost-effective, secure, and fast applications that solve customer pain points. So, if you are a company or an individual who wants to explore blockchain technology, this article will help you understand blockchain nodes and their importance.




![How to set up a Raspberry Pi web server in 2021 [Guide]](https://i0.wp.com/pcmanabu.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/web-server-02-309x198.png?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)












































