YAML Ain’t Markup Language (YAML) is a data serialization language for most programming languages. Let’s understand in detail.
YAML is a strict superset of JSON , so anything written in JSON can be parsed to YAML . It is mainly used for project configuration files and makes the code very easy to understand and read.
The file extension for YAML files is .yaml or .yml .
In this tutorial, you will learn about the different data types that exist in YAML and work with YAML in Python. After completing this tutorial, you will be able to understand YAML and its syntax.
Even if you haven’t looked into Python learning resources, you’re probably already familiar with Python.
YAML follows an indentation syntax similar to Python. However, you cannot use tabs for indentation (keep that in mind when creating YAML files).

setting
- To work with YAML files, install a Python module called
pyyaml.
pip install pyyaml- Copy and paste the following code into the file and save it as
yaml_script.py.
import yaml
yaml_file = open("learn_yaml.yaml", 'r')
yaml_content = yaml.load(yaml_file)
print("Key: Value")
for key, value in yaml_content.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")- Use the above script to convert YAML code to Python and explore different data types.
- Create a file called
learn_yaml.yamland practice the various examples covered in this tutorial in it.
Let’s move on to the YAML data types section.

YAML data types
Everything in YAML is a key-value pair.
Different programming languages have different names for key-value pairs, such as dictionaries, hashes, and objects. These are the building blocks of YAML.
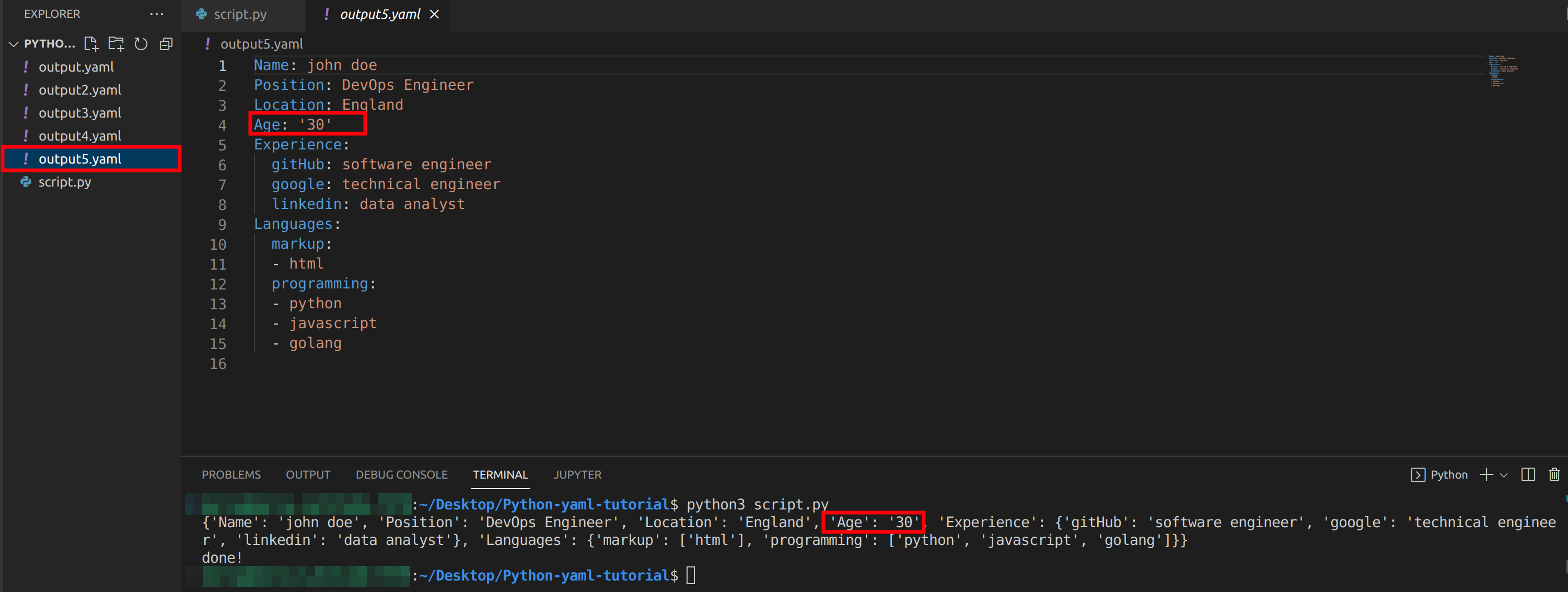
Keys can be strings (quoted or regular), floats, or integers (support may change in future updates). Additionally, the value can be any data type supported by YAML.
Let’s take a look at the different data types that exist in YAML.
numbers
YAML supports integers, floats, and exponential floats.
integer: 123
float: 123.123
exponential_float: 1.34e+3If you evaluate the above code in a Python script, you will get the following result:
Key: Value
integer: 123
float: 123.123
exponential_float: 1340.0Values can be represented in different number systems such as decimal, octal, and hexadecimal .
- A leading zero (0) indicates an octal number.
- The prefix 0x represents a hexadecimal value.
See example below.
integer: 123
octal: 0123
hexa: 0x123By running the Python script, you can see the decimal value after converting the octal and hexadecimal values. You should see exact output similar to the following:
Key: Value
integer: 123
octal: 83
hexa: 291Another interesting thing about YAML is that it can represent NAN (Not A Number) and Infinity .
not_a_number: .NAN
infinity: .inf
negative_infinity: -.infWhen you run the Python script, you will see the NAN and inf conversion values to Python.
Key: Value
not_a_number: nan
infinity: inf
negative_infinity: -infThat’s all about YAML numeric types.
string
YAML strings can be expressed with or without quotes . Both are similar. Unlike JSON, there is no hard and fast rule to enclose all strings in quotes. However, if you need to use escape sequences , you must use double quotes .
Let’s look at some string examples.
string: Hi, there I am a string
string with escape character: Hi, I am a newline \n character. And I am not working :(
string with working escape character: "Hi, I am a newline \n character. And I am working :)"Newline characters in section key-value pairs work as expected. As already mentioned, double quotes must be used to work with escape sequences.
I used double quotes in the following key-value pair and it works as expected. Interpret the above YAML code with a Python script. You will get the result as follows:
Key: Value
string: Hi, there I am a string
string with escape character: Hi, I am a newline \n character. And I am not working :(
string with working escape character: Hi, I am a newline
character. And I am working :)YAML has two special characters that you can use to write multiple statements as values for keys. Suppose you need to split a long sentence into multiple lines. In this type of scenario, you can use fold (> >) or block (pipe |) characters to write multiple lines.
What is the difference between folded letters and block letters?It’s finally time.
Folding characters do not interpret line breaks, but block characters do.
Let’s look at an example.
multiple lines string with fold character: >
This is a
multiple line
string with fold
character. Remember to use
indentation. Newlines won't be
interpreted.
multiple lines string with block character: |
This is a
multiple line
string with fold
character. Remember to use
indentation. Newlines will be
interpreted.You can tell the difference between crease characters and block characters by running the Python script. Don’t forget to use indentation.
Key: Value
multiple lines string with fold character: This is a multiple line string with fold character. Remember to use indentation. Newlines won't be interpreted.
multiple lines string with block character: This is a
multiple line
string with fold
character. Remember to use
indentation. Newlines will be
interpreted.boolean value
YAML allows you to represent the boolean values True and False in three different ways. Please take a look.
- The values True, On, and Yes are considered True in YAML.
- The values False , Off , and No are considered False in YAML.
random_key_1: True
random_key_2: On
random_key_3: Yes
random_key_4: False
random_key_5: Off
random_key_6: NoInterpreting the above YAML code, the first three key values are retrieved as True and the next three key values are retrieved as False .
Key: Value
random_key_1: True
random_key_2: True
random_key_3: True
random_key_4: False
random_key_5: False
random_key_6: Falsenull
YAML, like JSON, supports null values. You can define null values in YAML using the keyword null or the symbol tilde (~) . There are quite a few alternatives to YAML, right? Well, they’re kind of cool.
null_case_1: null
null_case_2: ~Run the Python script. Python uses None instead of the null keyword, so both values are retrieved as None .
Key: Value
null_case_1: None
null_case_2: Nonearray
YAML allows you to specify arrays similar to Python. Alternatively, you can put all array elements on separate lines, preceded by a hyphen (-) . Let’s look at an example of each expression.
programming_languages: [Python, JavaScript, C, HTML, CSS]
libraries: [React, TailwindCSS]In the YAML code above, I used square brackets similar to Python lists. Let’s look at another way to represent arrays in YAML, which looks like a markdown list.
programming_languages:
- Python
- JavaScript
- C
- HTML
- CSS
libraries:
- React
- TailwindCSSIf you want to interpret the above example using a Python script. You will get output like this:
programming_languages: [Python, JavaScript, C, HTML, CSS]
libraries: [React, TailwindCSS]Lists can contain not only strings, numbers, etc., but also dictionaries.
programming_languages: - Python: author: Guido van Rossum - JavaScript: author: Brendan Eich - C: author: Dennis Ritchie libraries: - React: popularity: High - TailwindCSS: popularity: High
Interpreting the above YAML code with a Python script will give you an array of dictionaries.
Key: Value
programming_languages: [{'Python': {'author': 'Guido van Rossum'}}, {'JavaScript': {'author': 'Brendan Eich'}}, {'C': {'author': 'Dennis Ritchie'}}]
libraries: [{'React': {'popularity': 'High'}}, {'TailwindCSS': {'popularity': 'High'}}]dictionary
We have already seen the dictionary syntax in the example above. To summarize briefly, a dictionary is a key-value pair. You can use any valid data type as the key value. YAML also supports nested dictionaries.
Let’s look at an example.
dictionary:
i am key: i am value
nested dictionary:
nested key:
i am nested key: i am nested valueIf you interpret the above code, you will see the same result as below:
Key: Value
dictionary: {'i am key': 'i am value'}
nested dictionary: {'nested key': {'i am nested key': 'i am nested value'}}Did you know you can convert a list to a dictionary in Python?
set
YAML supports another data type called a set. A Set contains unique values, similar to Python’s set data type. Just as list items are preceded by a hyphen (-) , configuration items are preceded by a question mark (?) .
It should be noted that the data type is set using !!set after the set name.
Take a look at the following example.
i am a set: !!set
? 1
? 2
? 2
? 3If you interpret the above YAML code in a Python script, you will not get 2 twice, because set only contains unique values.
Let’s see the results.
Key: Value
set: {1, 2, 3}You can also express sets similar to Python syntax, as follows:
i am a set: !!set
{1, 2, 2, 3}You will get exactly the same output as the example above.
That’s all about YAML data types. Let’s take a look at some additional features of YAML.
comment
YAML supports comments. that’s great. YAML allows you to write comments starting with a hash (#) symbol.
# I am a comment
yaml is great: # I am a comment tooWhen you interpret the YAML code above, you will get an empty key with a null value.
Key: Value
yaml is great: NoneYAML does not support multiline comments. Similar to Python, for multi-line comments, you need to write multiple lines starting with the hash.

anchor
Anchors allow you to copy the contents of a key anywhere throughout the document. This is very useful when you want to duplicate some content within a document.
To use an anchor, you must define the name of the anchor as a variable name in the programming language. And you can use it anywhere you want throughout the document.
You can use & to define an anchor name and use it with * . Let’s look at an example.
# duplicate_data is the name of the anchor
data: &duplicate_data This content is to duplicate
# dopying the data
duplicate_data: *duplicate_dataIn the example above, we used the duplicate_data anchor to copy the data key value. Interpreting the above YAML, both keys contain the same value.
Key: Value
data: This content is to duplicate
duplicate_data: This content is to duplicateconclusion
I hope you have a good understanding of YAML. You can now use YAML in the following project configuration files: For more advanced content, please refer to the official YAML website.
Have fun coding 🙂





![How to set up a Raspberry Pi web server in 2021 [Guide]](https://i0.wp.com/pcmanabu.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/web-server-02-309x198.png?w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)












































